Reprogramming Cell Fate
Reporter: Larry H.Bernstein, MD, FCAP
- the inactivation of one is necessary for cell differentiation.
- Only after epigenetic reprogramming of the X chromosome can pluripotency be acquired.
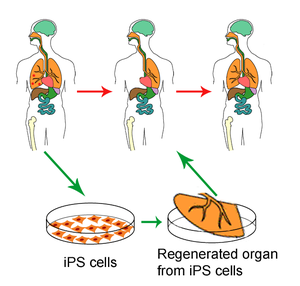
Pluripotent stem cells can generate – any fetal or adult cell type but
- don’t develop into a complete organism.
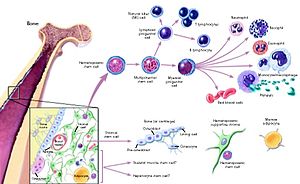
Multicellular organisms consist of
- functionally distinct cellular types
- produced by differential activation of gene expression.
The pioneer factor, discovered by Prof. KS Zaret at UPenn SOM in 1996, endows the competence for gene activity,
- being among the first transcription factors to
- engage and pry open the target sites in chromatin.
- induction of the liver program.
- nearly one-third of the DNA sites bound by FoxA in the adult liver occur near silent genes.
Related articles
- Neurons can be reprogrammed long after they’ve matured, study finds (rawstory.com)
- Reprogramming cells to fight diabetes (scienceblog.com)
- New Study Sheds Light On Cellular Reprogramming (medicalnewstoday.com)
- Pancreatic Cells Reprogrammed By Epigenetic Alterations To Secrete Insulin (medicalnewstoday.com)
- New light shed on reprogramming mature cells to pluripotency, to divide and differentiate into specialized cell types (sciencedaily.com)